Local weather and setting researcher
 Getty Photographs
Getty PhotographsThe world’s glaciers are melting quicker than ever recorded below the affect of local weather change, based on probably the most complete scientific evaluation so far.
Mountain glaciers – frozen rivers of ice – act as a freshwater useful resource for tens of millions of individuals worldwide and lock up sufficient water to lift international sea-levels by 32cm (13in) in the event that they melted completely.
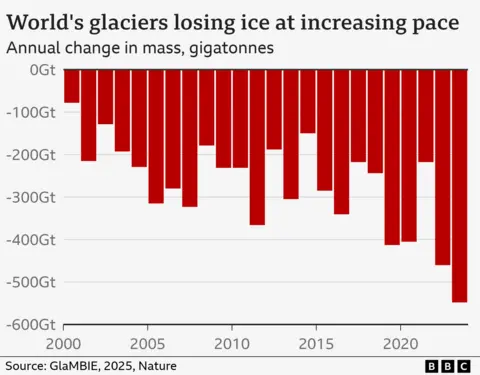
However for the reason that flip of the century, they’ve misplaced greater than 6,500 billion tonnes – or 5% – of their ice.
And the tempo of melting is rising. Over the previous decade or so, glacier losses have been greater than a 3rd increased than through the interval 2000-2011.
The examine mixed greater than 230 regional estimates from 35 analysis groups around the globe, making scientists much more assured about precisely how briskly glaciers are melting, and the way they are going to evolve sooner or later.
Glaciers are glorious indicators of local weather change.
In a steady local weather, they continue to be roughly the identical measurement, gaining about as a lot ice via snowfall as they lose via melting.
However glaciers have been shrinking just about in all places over the previous 20 years as temperatures have risen attributable to human actions, principally burning fossil fuels.
Between 2000 and 2023, glaciers exterior the foremost ice-sheets of Greenland and Antarctica misplaced round 270 billion tonnes of ice a 12 months on common.
These numbers aren’t straightforward to get your head round. So Michael Zemp, director of the World Glacier Monitoring Service and lead creator of the examine, makes use of an analogy.
The 270 billion tonnes of ice misplaced in a single 12 months “corresponds to the [water] consumption of the complete international inhabitants in 30 years, assuming 3 litres per particular person and day”, he instructed PJDM Information.
The speed of change in some areas has been notably excessive. Central Europe, for instance, has misplaced 39% of its glacier ice in little over 20 years.
The novelty of this examine, published in the journal Nature, will not be a lot discovering that glaciers are melting quicker and quicker – we already knew that. As an alternative, its energy lies in drawing collectively proof from throughout the analysis group.
There are numerous methods of estimating how glaciers are altering, from area measurements to several types of satellite tv for pc knowledge. Every has its personal benefits and drawbacks.
Direct measurements on glaciers, for instance, give very detailed info, however are solely out there for a tiny fraction of the greater than 200,000 glaciers worldwide.
By systematically combining these totally different approaches, scientists may be way more sure about what is going on on.
These group estimates “are important as they provide individuals confidence to utilize their findings”, mentioned Andy Shepherd, head of the Division of Geography and Setting at Northumbria College, who was not an creator of the current examine.
“That features different local weather scientists, governments, and trade, plus after all anybody who is worried concerning the impacts of worldwide warming.”
Glaciers take time to totally reply to a altering local weather – relying on their measurement, anyplace between just a few years and plenty of a long time.
Which means they are going to proceed to soften within the years forward.
However, crucially, the quantity of ice misplaced by the tip of the century will strongly depend upon how a lot humanity continues to heat the planet by releasing carbon dioxide and different greenhouse gases.
This could possibly be the distinction between shedding 1 / 4 of the world’s glacier ice, if international local weather targets are met, and almost half if warming continues uncontrolled, the examine warns.
“Each tenth of a level of warming that we will keep away from will avoid wasting glaciers, and can save us from a variety of injury,” Prof Zemp defined.
These penalties transcend native adjustments to landscapes and ecosystems – or “what occurs on the glacier does not keep there”, as Prof Zemp places it.
A whole lot of tens of millions of individuals worldwide rely to some extent on seasonal meltwater from glaciers, which act like big reservoirs to assist buffer populations from drought. When the glaciers disappear, so does their provide of water.
And there are international penalties too. Even seemingly small will increase to international sea-level – from mountain glaciers, the foremost Greenland and Antarctic ice-sheets, and hotter ocean waters taking on extra space – can considerably enhance the frequency of coastal flooding.
“Each centimetre of sea-level rise exposes one other 2 million individuals to annual flooding someplace on our planet,” mentioned Prof Shepherd.
International sea-levels have already risen by greater than 20cm (8in) since 1900, with round half of that coming for the reason that early Nineties, and quicker will increase are anticipated within the a long time forward.

#Local weather #change #Worlds #glaciers #melting #quicker #recorded
, 2025-02-19 16:23:00


