Your assist helps us to inform the story
From reproductive rights to local weather change to Massive Tech, The Unbiased is on the bottom when the story is growing. Whether or not it is investigating the financials of Elon Musk’s pro-Trump PAC or producing our newest documentary, ‘The A Phrase’, which shines a lightweight on the American ladies combating for reproductive rights, we all know how vital it’s to parse out the info from the messaging.
At such a crucial second in US historical past, we’d like reporters on the bottom. Your donation permits us to maintain sending journalists to talk to each side of the story.
The Unbiased is trusted by Individuals throughout your complete political spectrum. And in contrast to many different high quality information retailers, we select to not lock Individuals out of our reporting and evaluation with paywalls. We consider high quality journalism ought to be obtainable to everybody, paid for by those that can afford it.
Your assist makes all of the distinction.
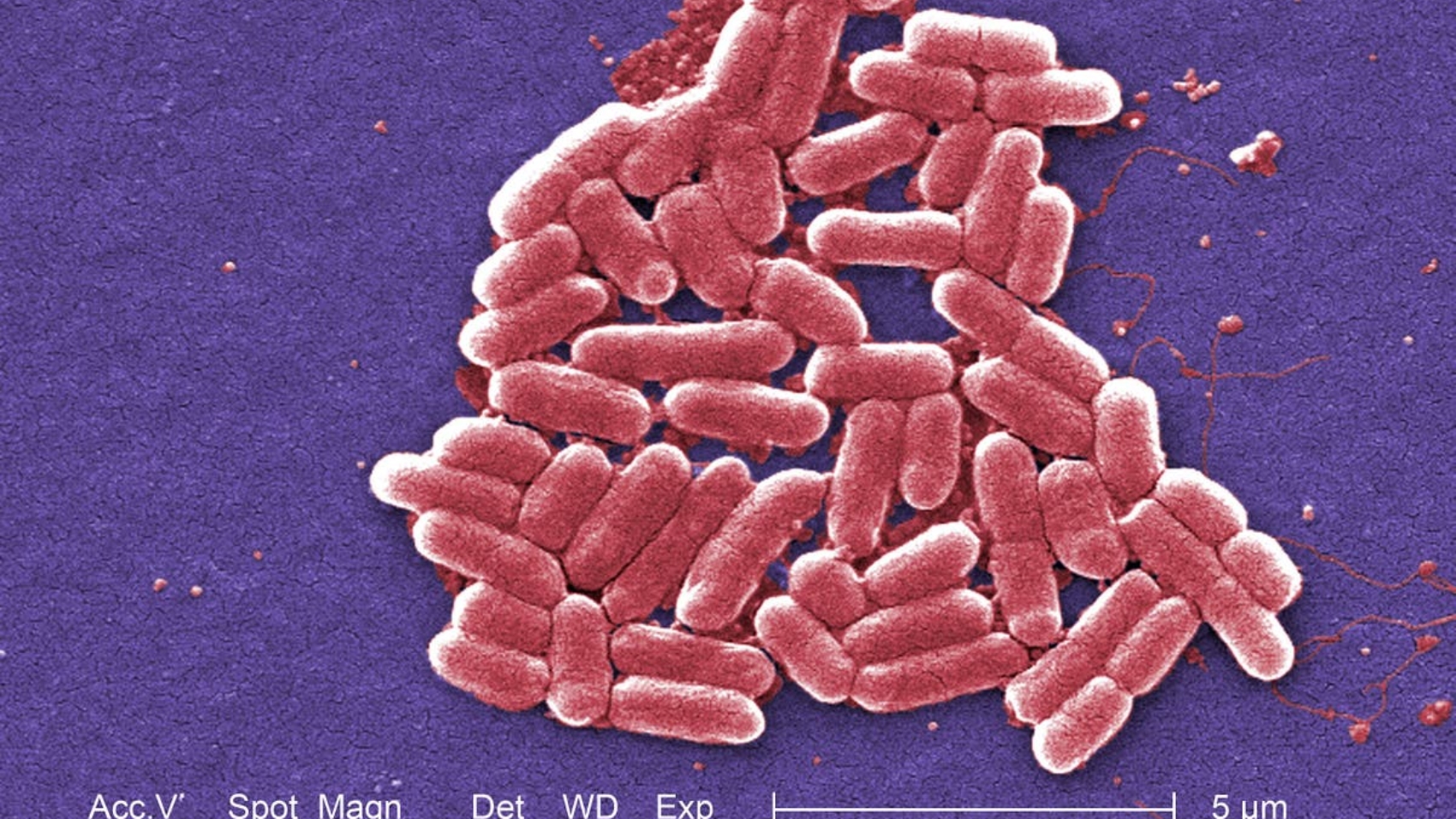
Vaccines concentrating on widespread intestine micro organism E.coli might scale back charges of colon most cancers in nations such because the UK, scientists have urged.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute have urged increased charges of colorectal, bladder and prostate cancers throughout industrialised nations might partially be defined by two strains of E.coli which trigger excessive charges of urinary tract infections and bloodstream infections.
In a paper, printed in The Lancet, scientists counsel a vaccine or probiotic which prevents these two strains from circulating might scale back the danger of most cancers. Nevertheless, they stress additional investigation could be wanted.
Professor Jukka Corander, senior creator from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, College of Oslo and the College of Helsinki, stated: “We now have been utilizing large-scale genomics to trace E. coli strains throughout a number of nations for the final 5 years, utilizing information that goes again to the early 2000s.
“This has allowed us to begin to see the doable connections between two E.coli strains and most cancers incidence charges.”
She added, “by working along with most cancers and microbiome consultants, we’re hopeful that sooner or later this work would possibly result in new methods to eradicate colibactin-producing E. coli strains.
“Vaccines or different interventions that concentrate on these E.coli strains might supply enormous public well being advantages. Comparable to lowering the burden of infections and lessening the necessity for antibiotics to deal with these, in addition to lowering the danger of cancers that might be linked to the consequences of colibactin publicity.”
The micro organism, E. coli, is often discovered within the human intestine. Most strains of E. coli are innocent; nonetheless, if the bacterium will get into the bloodstream as a result of a weakened immune system it will possibly trigger infections, starting from gentle to life-threatening.
The 2 strains of E.coli checked out by the researchers are the main reason behind UTIs and bloodstream infections throughout industrialised nations. Additionally they counsel concentrating on these micro organism might scale back antibiotic medicine use in industrialised nations.
Utilizing genomic surveillance information from nations together with the UK, Norway, Pakistan and Bangladesh researchers tracked the completely different strains of E.coli.
Earlier premilitary analysis means that two strains E.coli can produce a substance referred to as colibactin which performs a task within the growth of cancers of the urinary tract and have been linked to tumour samples from colon most cancers sufferers.
Evaluating the charges of those strains with most cancers charges they discovered industrialised counties the place these strains circulated additionally had increased ranges of bowel, bladder and prostate cancers.
Nevertheless in nations corresponding to Bangladesh and Pakistan these strains of E.coli had been a lot rarer as had been incidences of bowel, bladder and prostate cancers.
The paper suggests additional large-scale investigation is required, together with wide-spread tumour sampling, to make clear the function of colibactin in most cancers.
Dr Tommi Mäklin, first creator of the research, from the College of Helsinki and the Wellcome Sanger Institute, stated: “E. coli could be discovered around the globe, in many alternative types, and understanding how strains of this micro organism impression people in another way may give us a extra full image of well being and illness.
“Gaining access to international genomic information on which strains are present in an space can uncover new traits and potentialities, corresponding to strains in industrialised nations doubtlessly being linked to the danger of sure cancers. We additionally must maintain guaranteeing that nations and areas around the globe are included in genomic surveillance analysis so that everybody advantages from new discoveries.”
#Vaccine #concentrating on #widespread #intestine #micro organism #E.coli #stop #most cancers #scientists #counsel
The Unbiased
#Vaccine #concentrating on #widespread #intestine #micro organism #E.coli #stop #most cancers #scientists #counsel
Rebecca Thomas , 2024-12-04 23:52:00